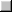 Date getDate()
Date getDate()Date()
|
syntax: |
new Date() new Date(milliseconds) new Date(string) new Date(year, month[, day[, hour[, minute[, second[, millisecond]]]]]) |
|
where: |
milliseconds - number of milliseconds since midnight January 1, 1970 GMT, as returned by Date.parse().
string - a string with date information. The string should be in the following format: Friday, October 31, 1998 15:30:00 GMT, or a substring of this format. The string accepted by Date() is the same as for Date.parse().
year - four digit year, see Date setYear(). If year is passed alone, it is recognized as milliseconds.
month - number, 0 - 11, month of year, see Date setMonth().
day - number, 1 - 31, day of month, see Date setDate().
hour - number, 0 - 24, hour of day, see Date setHours().
minute - number, 0 - 59, minute of hour, see Date setMinutes().
second - number, 0 - 59, second of minute, see Date setSeconds().
millisecond - number, 0 - 999, millisecond of second, see Date setMilliseconds().
|
|
return: |
object - a Date object set according to the arguments passed. If no arguments are passed, then the current date and time are set.
|
|
description: |
ScriptEase JavaScript has a rich set of methods for working with dates and times. The JavaScript Date object is a variable type that is different from the Clib date and time methods. The Date.fromSystem() and Date toSystem() methods allow conversion from and to the C style methods. See the Date Object for a complete description of the Date() function.
If the new operator is used, for example, new Date(1999, 2), then a Date object is created using any parameters passed to the Date() constructor. However, if the new operator is not used, then all parameters are ignored and Date() returns a string representation of the current date and time, for example, "Wed Sep 4 11:54:16 2002".
|
|
see: |
Date Object, Date toSystem(), Date.fromSystem(), Date object instance methods, Date object static methods, Clib.time(), Clib.gmtime(), Clib.localtime(), Clib.mktime()
|
|
example: |
var d = new Date() // date in a Date object // d == Mon Aug 20 16:29:53 2001 // ie, current // typeof(d) == object // d._class == Date var d = Date() // date as a String // d == Mon Aug 20 16:29:53 2001 // ie, current // typeof(d) == string // d._class == String var d = new Date().getDay() // d == 1 // which is Monday |